
Economists are predicting a mild recession in 2024. That means small to medium-sized businesses will have to work a little harder to stay profitable and successful. Luckily, we're breaking down three things businesses can do in 2024 to maximize opportunity and set their businesses up for 5-6 years of consecutive growth.
*all economic data was provided by ITR Economics*
What's Happening in the Economy
So right now, in 2023, we've passed through an inflection point, and the growth rate for the economy has peaked. Whether you're looking at GDP or manufacturing, the economy's growth rate has peaked, and economists are seeing growth rates slow down. The economy is still growing, but at a much slower pace. Slowing growth rates are a warning sign because typically, when we enter this part of the economic business cycle, that suggests a recession is coming our way.
What ITR Economics has seen in 2023 is a weakening of incoming business orders. They're seeing a pullback in CapEx as we all deal with higher interest rates as the federal reserves are trying to capture or bring down the higher level of inflation. So we're at that point in the cycle in 2023 where we're seeing all of these warning signs. The economy is still expected to grow throughout the remainder of 2023, just at a much slower pace than what businesses experienced in 2021 and 2022.
What Businesses Can Expect in 2024 and Beyond
The real challenge arrives as we get into next year. ITR Economics forecasts a recession in the economy in 2024. Again, whether you're looking at a series like industrial production, which highlights manufacturing, or whether you're looking at a broad base measure like GDP, the data is reflecting a recession.
Now, when someone uses the word recession, people's minds immediately go to the pandemic or the 2008 financial crisis – that is not the type of recession ITR Economics is projecting. This recession is projected to be very mild as the GDP will only be down about -0.3%. That is a very mild recession. But by definition, it's still a recession. So, business owners should expect to see some challenges next year – mainly due to this higher interest rate environment as businesses pull back in their investments and spending.
As we look out to 2025 and 2026, that's where the good news comes in! Economists see 2025 and 2026 growing at rates typical for a healthy US economy, looking at about 2.5% growth, for example, in 2025.
So, from a very high level, the way we're thinking about the next three to five years is that we'll see some challenges ahead, but this is a recession where we're urging everyone to be aggressive. Because the recession in 2024 is so mild, it should be a time when you're catching your breath, clearing the debris from the last few years, and making investments in your business so that you can capitalize on the growth that we have coming in 2025 and 2026. If businesses use 2024 correctly, they'll essentially be preparing their businesses for 5-6 years of consecutive growth.
After we encounter a mild recession in 2024, ITR Economics is not forecasting we witness another until 2030. Unfortunately, in 2030 they're forecasting a much worse economic outlook – describing this recession as a depression. If you're interested in laying out a long-term business plan in preparation for the 2030 depression, read more about ITR's forecast here and what you can do to plan ahead.
Rather focus on the year ahead of us? Read on to discover 3 ways to maximize opportunity in 2024!
3 tips For Maximizing Opportunity During the Mild Recession Expected in 2024:

1. Look for Countercyclical Markets
Countercyclical markets refer to segments of the economy that tend to perform well when the broader economy is in a downturn or recession. These markets often exhibit an inverse relationship with the overall economic cycle, which means that when the economy is struggling, countercyclical markets tend to thrive. They can provide investors with opportunities for stability and potential returns, even when the general economic outlook is negative.
Here are a few examples of countercyclical markets:
Healthcare:
The healthcare industry is often considered countercyclical because people require medical services regardless of the economic conditions. In fact, healthcare spending may even increase during recessions, as people prioritize their health and well-being.
Consumer Staples:
Companies that produce and sell essential items like food, beverages, toiletries, and household goods fall into the consumer staples category. These products are necessities, and demand for them remains relatively stable even during economic downturns.
Utilities:
Utilities, including companies that provide electricity, gas, and water services, are considered countercyclical because these services are essential and have consistent demand, irrespective of economic cycles.
Precious Metals:
Precious metals like gold and silver are often seen as safe-haven assets during economic crises. Their prices may rise when the economy is facing uncertainty or inflation, making them countercyclical investments.
Discount Retailers:
Discount retailers, which offer affordable products and services, can see increased business during economic downturns as consumers look for ways to save money.
It's important to note that while these markets are considered countercyclical, they are not immune to economic fluctuations, and their performance can be influenced by various factors. Additionally, not all companies within these sectors may be countercyclical, so it's crucial for investors to conduct thorough research and consider individual company performance and financial health when making investment decisions.
2. Eliminate Unprofitable Business Segments
Get rid of things! Remove products that don't have the margin profiles you need. Get your house in order and eliminate wasted space and wasted costs while growth rates are down in 2024. When you have a solid foundation built on profitable products, it will feel like an easier path to growth. Identifying unprofitable products or business segments is a crucial step in optimizing your business's performance and profitability. Here's a checklist to help you determine unprofitable products or segments:
Financial Analysis:
-
- Compare revenue generated by each product or segment against their respective costs.
- Calculate gross profit margins for each product or segment (Gross Profit = Revenue - Cost of Goods Sold).
- Calculate net profit margins (Net Profit = Revenue - All Costs, including operating expenses) for each product or segment.
- Ensure that all costs, including overhead, are accurately allocated to each product or segment. Sometimes, certain costs can be hidden or incorrectly attributed.
- Calculate the break-even point for each product or segment to determine the level of sales required to cover costs. If a product or segment consistently falls below this point, it may be time to consider cutting it.
- Analyze the sales volume and growth trends for each product or segment. Declining or stagnant sales may indicate an unprofitable product.
- Assess the profitability of customers associated with each product or segment. Some customers may generate higher profit margins than others. Consider if unprofitable products are primarily sold to unprofitable customers.
- Analyze inventory turnover rates and carrying costs. Products that have slow turnover or high carrying costs may be unprofitable.
- Evaluate your pricing strategy for each product or segment. If you consistently offer discounts or promotions to sell a product, it may not be profitable.
- Consider the competitive landscape and market trends for each product or segment. If competitors offer similar products at lower prices or if the market is shrinking, it may be difficult to maintain profitability.
- Evaluate the operational efficiency and production costs for each product or segment. Identify any areas where efficiency improvements can reduce costs.
- Review the marketing and sales efforts for each product or segment. High marketing and sales costs relative to revenue may indicate unprofitability.
- Gather customer feedback and reviews for each product or segment. Negative feedback or consistently low customer satisfaction may signal issues with a product's profitability.
- Consider the product's or segment's lifecycle and future prospects. If it's a declining market with no potential for growth, it may not be worth sustaining.
- Assess the opportunity costs associated with unprofitable products or segments. Could resources and efforts be better allocated elsewhere?
- Evaluate whether the product or segment aligns with your overall business strategy and goals. Sometimes, unprofitable products or segments may not fit your long-term vision.
- Consider different scenarios, such as cost reductions or pricing adjustments, to see if unprofitable products or segments can be turned around.
-
- Regularly review the profitability of products and segments. What may be unprofitable today might change with market conditions or internal improvements.
Consult with Experts:
- Seek the advice of financial analysts, consultants, or industry experts to get an objective assessment of your products or segments.
Exit Strategy:
- Develop an exit strategy for unprofitable products or segments, which may include phasing them out, selling them, or spinning them off into a separate entity.
Remember that the decision to discontinue or revamp a product or business segment should be based on a careful analysis of these factors and should align with your overall business strategy. Additionally, consider the impact on employees, customers, and stakeholders when making such decisions.
3. Build Cash Reserves
Cash is the lifeblood of any business. Without cash, an organization can't afford to keep its day-to-day operations running. Cash is important for two reasons; it offers flexibility to make investments for the future, and it offers security to be able to weather storms. Cash reserves are a great way to ensure an organization can stand the test of time or endure a crisis. So, it's always a good practice to accumulate cash during periods of economic growth to better prepare for downturns. Look to tuck cash away in 2025 and 2026 as we'll be experiencing healthy economic growth.
Here are some steps to help you build cash reserves in your business:
Cut Unnecessary Expenses:
Review your budget and identify areas where you can reduce or eliminate expenses. This might involve renegotiating contracts, cutting non-essential services, or finding more cost-effective suppliers.
Increase Revenue:
Explore ways to increase your revenue, such as expanding your customer base, introducing new products or services, or implementing marketing strategies to boost sales.
Set Aside a Portion of Profits:
Commit to setting aside a percentage of your profits as cash reserves. The exact percentage can vary depending on your business's needs and goals. Many financial experts recommend setting aside at least 10% of your profits.
Automate Savings:
Consider setting up an automated transfer from your operating account to your cash reserve account. This ensures that you consistently contribute to your reserves without having to think about it.
Monitor and Adjust:
Regularly review your budget and financial statements to ensure you're on track to meet your cash reserve goals. Adjust your savings rate as your business's financial situation changes.
-1.png?width=80&height=80&name=Coachs%20Tip%20Chat%20Bubble%20(1)-1.png)
7 Ways To Improve Cash Flow In Your Business
Prioritize Debt Reduction:
Reducing or eliminating high-interest debt can free up more cash for savings. Focus on paying down loans or credit card balances, as this can both decrease interest payments and improve your financial stability.
Plan for Taxes:
Be sure to budget and save for taxes throughout the year to avoid any unexpected cash flow issues when tax time arrives.
Continuously Improve Efficiency:
Seek ways to make your business more efficient. Streamlining operations can reduce costs and increase profitability, which, in turn, can help you build cash reserves.
Consider Diversification:
Explore investment options for your cash reserves to generate some returns while keeping funds accessible. Talk to a financial advisor to determine the best options for your business.
Reinvest Wisely:
When you do use your cash reserves, do so wisely. Invest in activities or assets that will contribute to the long-term growth and sustainability of your business.
-1.png?width=80&height=70&name=Chat%20Bubble%202%20(1)-1.png) Forecast and Predict Cash Flow with Our Cash Flow Calculator
Forecast and Predict Cash Flow with Our Cash Flow Calculator
Remember that building cash reserves is a gradual process, and it may take time to accumulate a significant amount. The key is to be disciplined and consistent in your savings efforts while remaining flexible to adapt to changing financial circumstances. Cash reserves can provide peace of mind and financial security for your business, making it well-prepared for unexpected challenges.
Develop Your Strategy For Growth!
Build a short and long-term strategy with our High-Involvement Planning™ playbook.
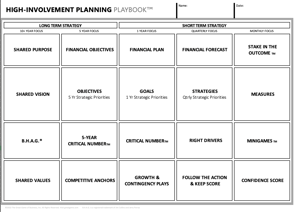
Want help building a long-term plan? Try our business planning workshop!
.png)





.png)




-5.png)
.png)
